
2 月 . 15, 2025 11:09 Back to list
california distributed energy storage
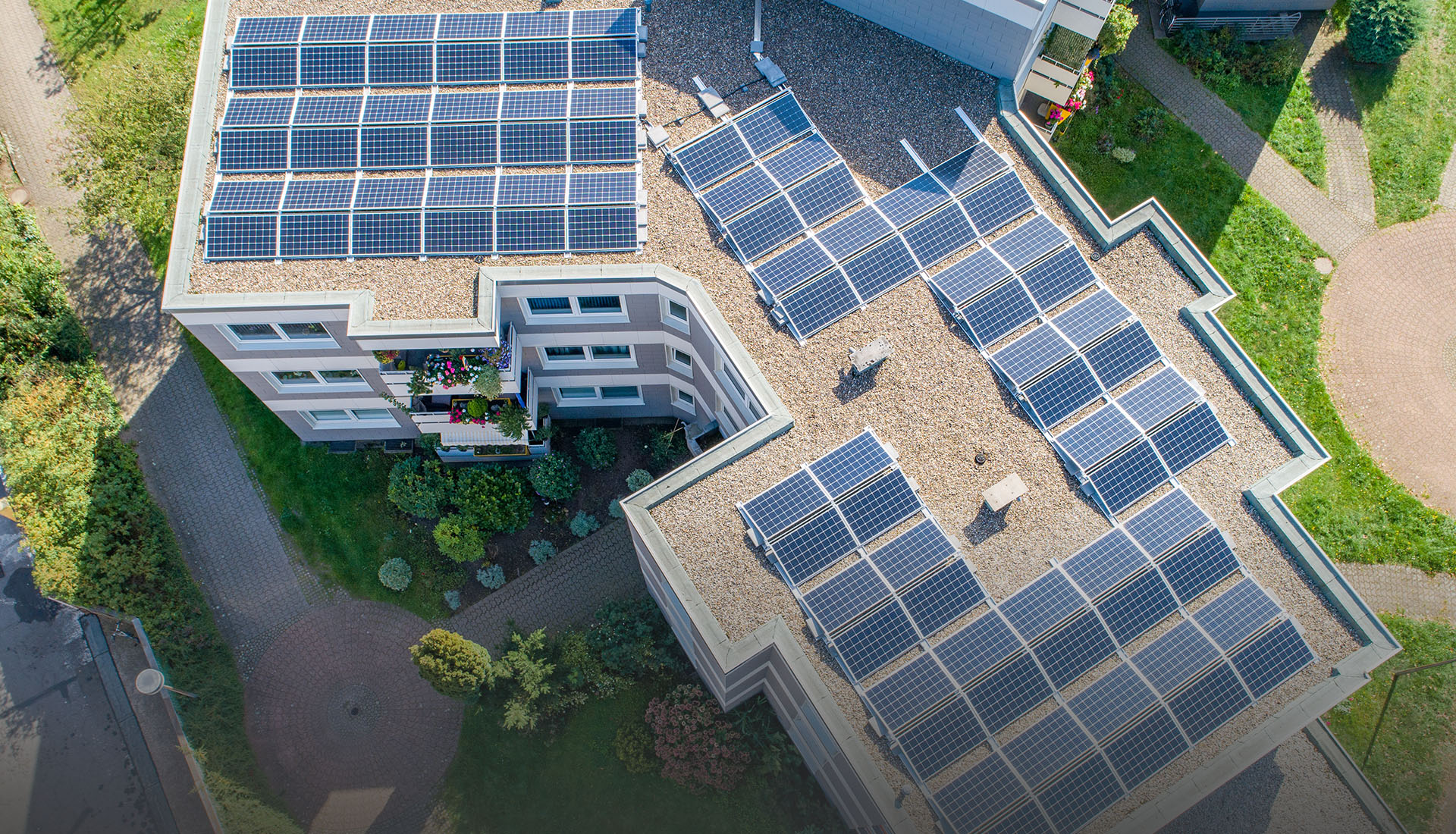
California's distributed energy storage landscape is undergoing a dynamic transformation fueled by technological advancements and legislative initiatives. As energy demands surge and environmental concerns necessitate cleaner alternatives, distributed energy storage emerges as a critical component in the Golden State's energy strategy. This article delves into the nuances of distributed energy storage, exploring its applications, benefits, and the evolving regulatory framework that fosters its adoption.
Regulatory frameworks play an instrumental role in accelerating the adoption of distributed energy storage in California. The Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) is a noteworthy initiative, offering financial incentives for installing eligible distributed energy systems. This scheme not only makes the initial investment more palatable but also incentivizes innovation in energy storage technologies. Furthermore, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) has mandated that the state's major utilities integrate storage solutions into their resource planning. By setting procurement targets for energy storage, the commission ensures a steady momentum towards a resilient and sustainable grid. The regulatory impetus is complemented by the state's overarching goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2045, a target that hinges on widespread energy storage deployment. Despite the promising outlook, the distributed energy storage market faces certain challenges. The initial capital cost of energy storage systems can be a barrier, particularly for small-scale installations. However, declining battery prices and enhancing economies of scale present a positive trajectory for cost reductions. Additionally, advancements in battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, hold the potential to revolutionize the storage landscape by offering improved safety and longer lifespans. Another challenge lies in the integration of distributed storage with existing grid infrastructure. Overcoming technical barriers, such as interoperability and standardization, is essential to fully realize the benefits of decentralized storage solutions. Industry collaboration and continued investment in research and development are keys to overcoming these hurdles. In conclusion, California stands at the forefront of the distributed energy storage revolution, driven by a confluence of innovative products, supportive policies, and an unwavering commitment to sustainability. By embracing distributed energy storage, the state not only fortifies its energy security but also paves the way for a greener, more resilient future. As technology continues to evolve and regulatory landscapes adapt, California's experience offers valuable insights for other regions poised to embark on their own energy storage journeys.

Regulatory frameworks play an instrumental role in accelerating the adoption of distributed energy storage in California. The Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) is a noteworthy initiative, offering financial incentives for installing eligible distributed energy systems. This scheme not only makes the initial investment more palatable but also incentivizes innovation in energy storage technologies. Furthermore, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) has mandated that the state's major utilities integrate storage solutions into their resource planning. By setting procurement targets for energy storage, the commission ensures a steady momentum towards a resilient and sustainable grid. The regulatory impetus is complemented by the state's overarching goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2045, a target that hinges on widespread energy storage deployment. Despite the promising outlook, the distributed energy storage market faces certain challenges. The initial capital cost of energy storage systems can be a barrier, particularly for small-scale installations. However, declining battery prices and enhancing economies of scale present a positive trajectory for cost reductions. Additionally, advancements in battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, hold the potential to revolutionize the storage landscape by offering improved safety and longer lifespans. Another challenge lies in the integration of distributed storage with existing grid infrastructure. Overcoming technical barriers, such as interoperability and standardization, is essential to fully realize the benefits of decentralized storage solutions. Industry collaboration and continued investment in research and development are keys to overcoming these hurdles. In conclusion, California stands at the forefront of the distributed energy storage revolution, driven by a confluence of innovative products, supportive policies, and an unwavering commitment to sustainability. By embracing distributed energy storage, the state not only fortifies its energy security but also paves the way for a greener, more resilient future. As technology continues to evolve and regulatory landscapes adapt, California's experience offers valuable insights for other regions poised to embark on their own energy storage journeys.
Latest news
-
FREMO Portable Power Station High-Capacity, Lightweight & Reliable
NewsMay.30,2025
-
24V DC Power Supply Certified & Efficient Home Depot Exporters
NewsMay.30,2025
-
12V 2A DC Power Supply for Home Depot Trusted Supplier & Exporter
NewsMay.29,2025
-
Energy Storage Power Station Solutions Reliable & Efficient Products
NewsMay.29,2025
-
Portable Power Station R100 High-Capacity & Reliable Backup Power
NewsMay.29,2025
-
Energy Management System EMS
NewsMar.07,2025


